Stop Worrying and Start Isolating – Limiting Removable Media Always Fails
May 28, 2024Target: IT Professionals (Elementary)
Tags: Phishing, Safe Workspace®, Safe Browsing, NoCloud® Protection by containment™
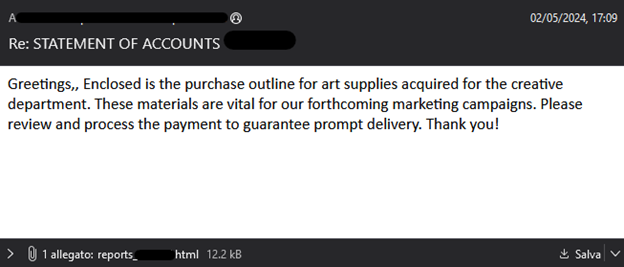
Using portable media, such as USB drives, is paramount in enterprise cybersecurity. Nevertheless, these devices also potentially threaten sensitive data and networks. Organizations must establish a comprehensive strategy for safeguarding against potential attacks. It is crucial to acknowledge the intricacies involved in effectively mitigating these threats.
Understanding the Threat Landscape
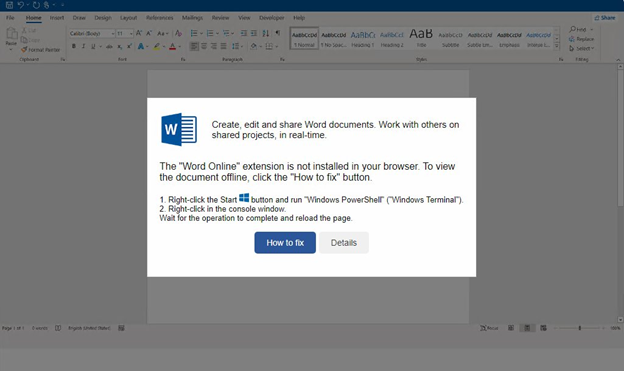
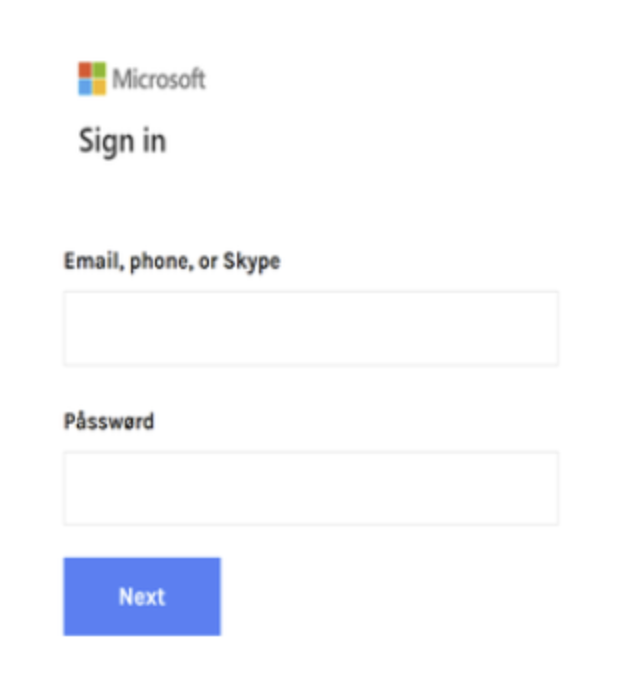
Removable media presents both a convenient and risky option for data transfer. While it enables seamless sharing, it also poses a security threat by acting as a potential entry point for malicious actors to infiltrate corporate networks. The risks associated with removable media are extensive, including malware infiltration, data theft, and exploitation of system vulnerabilities. Recent high-profile incidents have underscored the severity of unmonitored removable media usage and its potential consequences.
Challenges in Defense
Defending against removable media attacks poses significant challenges for enterprise users and security professionals. Traditional security measures such as antivirus software and perimeter defenses must often be equipped to thwart sophisticated attacks originating from removable media. The transient nature of these devices, coupled with their propensity to bypass traditional security mechanisms, renders enterprises vulnerable to infiltration and compromise.
Current Protections and Limitations
Due to the increasing threat landscape, organizations have implemented measures to reduce the security risks associated with removable media. However, there are better solutions than outright blocking or limiting the use of these devices, as it hinders productivity and collaboration and causes frustration for users but does not address the underlying security vulnerabilities.
While device control software can limit access, the pressure from employees and key management in the organization to enable users to work and connect removable media makes it difficult to maintain control. Consequently, CISOs (Chief Information Security Officers) and IT managers are forced to cancel device control limitations, exposing the organization to dangerous security risks.
The Solution: Prevention-Based Isolation
Removable media poses a significant threat to data security, but there’s hope in the form of prevention-based isolation. BUFFERZONE® Safe Workspace® security suite (that it’s strategic concept is Protection by containment™) takes a unique approach to removable media isolation, effectively neutralizing attacks from USB drives, CDs, and DVDs.
By creating a secure virtual environment that isolates removable media from critical systems and networks, BUFFERZONE® empowers organizations to utilize removable media without compromising security. Safe Workspace automatically opens removable media inside the secure virtual container, preventing auto-execution attacks.
Rather than outright blocking users access, BUFFERZONE® isolates the threat, allowing the user to work securely inside the container and open and edit media and documents without the risk of ransomware, data stealers, or other evasive attacks. Advanced detection solutions and antivirus software can scan the virtual environment and enhance security.
Making Security Accessible: Moving files from removable media to the organization
BUFFERZONE® SafeBridge® platform provides advanced file security features such as Content Disarm and Reconstruction (CDR). This feature is based on zero-trust principles and can protect organizations from unknown threats while allowing users to upload files into the organization safely.
SafeBridge® benefits organizations that use data sanitization KIOSKs, as it eliminates the need for users to go to the sanitization room and KIOSK station physically. Safe Workspace automatically secures removable media and moves it to the organization’s chosen location. This makes it easier and faster for users to access files without compromising security.
In addition to CDR, SafeBridge® also offers integration with multiple anti-virus scanners and malware sandboxes to provide even more robust security measures.
Conclusion
As the reliance on removable media continues to pervade enterprise environments, the imperative for robust security measures has never been greater. By acknowledging the inherent risks and embracing innovative solutions such as prevention-based isolation, organizations can confidently navigate the complexities of defending against removable media attacks. BUFFERZONE® Security stands at the forefront of this endeavor, equipping enterprises with the tools and technologies needed to safeguard their digital assets in an ever-evolving threat landscape.