Re-thinking About Your Endpoint Security Strategy Against New Threats
August 4, 2023Target: Consumers
Tags: Zero-Trust, Isolation, Policy, CDR, Trust No File
On July 16, 2023, researchers at DOCGuard [1] uncovered an incidence of a ZIP Bomb malware attack. Despite being scanned by 61 different detection vendors on VirusTotal, only one initially flagged the malicious file. A ZIP Bomb, colloquially known as a decompression bomb or zip of death, is a malicious archive file engineered to cripple or even crash the program or system that attempts to access it. Its prime use is typically to disable antivirus software, thereby paving the way for additional malware threats to breach the system.
At the time of this article’s writing, the detection ratio has slightly improved to 10 out of 61 engines. While it is important to note that no detection method is infallible or offers 100% accuracy, this instance serves as a crucial reminder for security professionals. It highlights the persistent need for vigilance, and how critical it is to continually reassess and recalibrate endpoint security strategies in an era where threats are both diverse and highly sophisticated. However, The ZIP Bomb is just one case and many other evasive attacks from various file formats are used to attack the endpoint. The attacks may come from browsing, file download, file sharing, removable media, and email messages.
The Problem with Malware Detection
Malware detection relies on identifying known patterns, signatures, behaviors associated with malware and may use advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) detection engines. However, this model struggles with newer and more innovative forms of malware that are designed to evade detection. For instance, the ZIP Bomb mentioned is a prime example of such a threat, demonstrating the challenge in detecting harmful payloads disguised or hidden within compressed files. This highlights the need for a change in thinking away from a sole reliance on detection-based defenses to proactive and isolation-oriented defenses and the need to add them as part of your new security stack.
Introducing Application Isolation and Advanced Policy
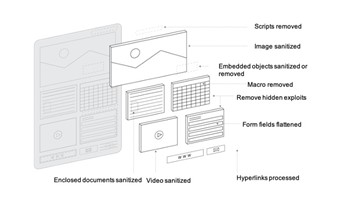
Endpoint security has seen a transformative approach through the introduction of application isolation, a method deeply rooted in the zero-trust model. This strategy aims to quarantine individual applications or programs from the broader system environment, effectively containing any potential threats and preventing their interaction with other “trusted” applications within the organization or the underlying system. This significantly curtails the possible ramifications of a security breach.
Consider, for instance, a web browser operating within this isolated environment. In a web-based attack, malicious activity is restricted within this isolated sphere, preventing any potential spread to the operating system or other applications. Therefore, even if a sophisticated piece of malware like a ZIP Bomb eludes initial detection, the damage it could inflict is confined to the isolated environment, neutralizing the threat.
Underpinning this approach is the integral role of endpoint security policies. These policies help to shrink your attack surfaces, thereby reducing the areas where your organization may be vulnerable to cyber threats and attacks. For example, application control settings can be employed as a proactive defense strategy, limiting the types of applications users can run and controlling the code that executes in the system’s core, or kernel. This level of regulation over application behaviors minimizes the overall exposure to potential threats. Furthermore, BUFFERZONE proprietary Firewall enables to control the endpoint communication network efficiently.
Taking this a step further, policies such as those enabled by BUFFERZONE can provide even greater specificity and control. For instance, they can allow for the installation of a certain verified file certificate, enabling the use of Microsoft’s proprietary applications while denying access to others, or blocking all user-downloaded applications altogether. This nuanced approach to application isolation further elevates the effectiveness of endpoint security.
Summary
In conclusion, given the rapidly evolving nature of cyber threats, adopting a security strategy that combines robust policy enforcement with application isolation is an effective approach. It allows an organization to not only defend against known threats but also mitigate the potential impact of unknown threats that evade traditional detection methods. This combination shifts the security paradigm from reactive detection to proactive containment, providing a more resilient defense against emerging threats.
References
[1] DOCGuard Zip Bomb Analysis, Docguard | Detects suspicious files!